Plant Regeneration Pathway
Plant Regeneration Pathway
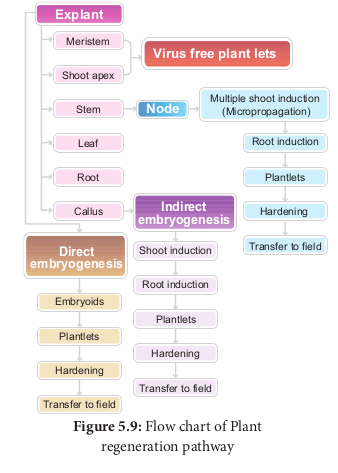
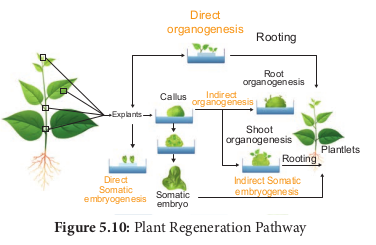
From the explants, plants can be regenerated by somatic embryogenesis or organogenesis.
Somatic Embryogenesis
Somatic embryogenesis is the formation of embryos from the callus tissue directly and these embryos are called Embryoids or from the in vitro cells directly form pre-embryonic cells which differentiate into embryoids.
Applications
- Somatic embryogenesis provides potential plantlets which after hardening period can establish into plants.
- Somatic embryoids can be be used for the production of synthetic seeds.
- Somatic embryogenesis is now reported in many plants such as Allium sativum, Hordeum vulgare, Oryza sativa, Zea mays and this possible in any plant.
Synthetic seeds are produced by encapsulation of embryoids in agarose gel or calcium alginate.
Organogenesis
The morphological changes occur in the callus leading to the formation of shoot and roots is called organogenesis.
Callus Differentiation Plantlets
Shoots (Caulogenesis)
Roots (Rhizogenesis)
- Organogenesis can be induced in vitro by introducing plant growth regulators in the MS medium.
- Auxin and cytokinins induce shoot and root formation.