Applications of Plant Tissue Culture
Applications of Plant Tissue Culture
Plant tissue culture techniques have several applications such as:
i. Improved hybrids production through somatic hybridization.
ii. Somatic embryoids can be encapsulated into synthetic seeds (synseeds). These encapsulated seeds or synthetic seeds help in conservation of plant biodiversity.
iii. Production of disease resistant plants through meristem and shoot tip culture.
iv. Production of stress resistant plants like herbicide tolerant, heat tolerant plants.
v. Micropropagation technique to obtain large numbers of plantlets of both crop and tree species useful in forestry within a short span of time and all through the year.
vi. Production of secondary metabolites from cell culture utilized in pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries.
Somaclonal variations:
Somatic variations found in plants regenerated in vitro (i.e. variations found in leaf, stem, root, tuber or propagule)
Gametoclonal variations:
Gametophytic variations found in plants regenerated in vitro gametic origin (i.e. variations found in gametes and gametophytes)
Micropropagation of Banana
Micropropagation of plants at industrial level maintains high standards of homogeneity in plants like pineapple, banana, strawberry and potato.

Artificial Seed
Artificial seeds or synthetic seeds (synseeds) are produced by using embryoids (somatic embryos) obtained through in vitro culture. They may even be derived from single cells from any part of the plant that later divide to form cell mass containing dense cytoplasm, large nuclceus, starch grains, proteins, and oils etc., To prepare the artificial seeds different inert materials are used for coating the somatic embryoids like agrose and sodium alginate.
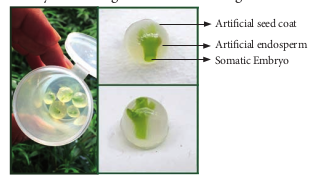
Advantages of Artificial seeds
Artificial seeds have many advantages over the true seeds
- Millions of artificial seeds can be produced at any time at low cost.
- They provide an easy method to produce genetically engineered plants with desirable traits.
- It is easy to test the genotype of plants.
- They can potentially stored for long time under cryopreservation method.
- Artificial seeds produce identical plants
- The period of dormancy of artificial seeds is greatly reduced, hence growth is faster with a shortened life cycle.
Virus-free plants
The field grown plants like perennial crops, usually are infected by variety of pathogens like fungi, bacteria, mycoplasma, viruses which cause considerable economic losses. Chemical methods can be used to control fungal and bacterial pathogens, but not viruses generally.
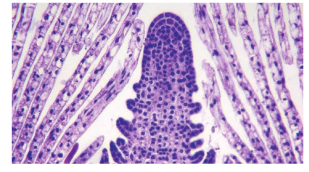
Shoot meristem tip culture is the method to produce virus-free plants, because the shoot meristem tip is always free from viruses.