NUCLEAR FUSION
When two or more light nuclei (A<20) combine to form a heavier nucleus, then it is called nuclear fusion. In the nuclear fusion, the mass of the resultant nucleus is less than the sum of the masses of original light nuclei. The mass difference appears as energy. The nuclear fusion never occurs at room temperature unlike nuclear fission. It is because when two light nuclei come closer to combine, they is strongly repelled by the coulomb repulsive force.
To overcome this repulsion, the two light nuclei must have enough kinetic energy to move closer to each other such that the nuclear force becomes effective. This can be achieved if the temperature is very much greater than 107 K. When the surrounding temperature reaches around 107K, lighter nuclei start fusing to form heavier nuclei and this resulting reaction is called thermonuclear fusion reaction.
Energy generation in stars:
The natural place where nuclear fusion occurs is the core of the stars, since their temperature is of the order of 107K. In fact, the energy generation in every star is only through thermonuclear fusion. In most of the stars including our Sun hydrogen atoms fuse into helium and in some stars helium atoms fuse into heavier elements.
The early stage of a star is in the form of cloud and dust. Due to their own gravitational pull, these clouds fall inward. As a result, its gravitational potential energy is converted to kinetic energy and finally into heat. When the temperature is high enough to initiate the thermonuclear fusion, they start to release enormous energy which tends to stabilize the star and prevents it from further collapse.
The sun’s interior temperature is around 1.5×10^7 K . In sun, 6×10^11 kg of hydrogen is converted into helium every second and sun has enough hydrogen such that these fusion reactions last for another 5 billion years. When the hydrogen is burnt out, the sun will enter into new phase called red giant where helium will fuse to become carbon. During this stage, sun will expand greatly in size and all its planets will be engulfed in it.
According to Hans Bethe, the sun is powered by proton-proton cycle of fusion reaction. This cycle consists of three steps and the first two steps are as follows:
2 3_H H He_+ → + γ (9.45)
A number of reactions are possible in the third step. But the most dominant one is
1 1_He He He H H_+ → + + (9.46)
The overall energy produced in the above reactions is about 27 MeV. The radiation energy we receive from the sun is due to these fusion reactions.
Elementary particles:
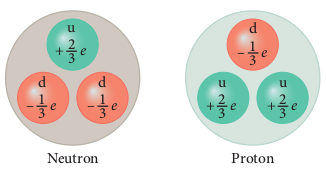
An atom has a nucleus surrounded by electrons and the nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. Till 1960s, it was thought that protons, neutrons and electrons are fundamental building blocks of matter. In 1964, physicists Murray Gellman and George Zweig theoretically proposed that protons and neutrons are not fundamental particles; in fact they are made up of quarks. These quarks are now considered elementary particles of nature. Electrons are fundamental or elementary particles because they are not made up of anything. In the year 1968, the quarks were discovered experimentally by Stanford Linear Accelerator Centre (SLAC), USA. There are six quarks namely, up, down, charm, strange, top and bottom and their antiparticles. All these quarks have fractional charges. For example, charge of up quark is + 2/3 e and that of down quark is - 1/3 e
According to quark model, proton is made up of two up quarks and one down quark and neutron is made up of one up quark and two down quarks as shown in the Figure 9.30.
The study of elementary particles is called particle physics and it is an active area of research even now. Till date, more than 20 Nobel prizes have been awarded in the field of particle physics.
Fundamental forces of nature:
It is known that there exists gravitational force between two masses and it is universal in nature. Our planets are bound to the sun through gravitational force of the sun. In +2 volume 1, we have learnt that between two charges there exists electromagnetic force and it plays major role in most of our day-to- day events. In this unit, we have learnt that between two nucleons, there exists a strong nuclear force and this force is responsible for stability of the nucleus. In addition to these three forces, there exists another fundamental force of nature called the weak force. This weak force is even shorter in range than nuclear force. This force plays an important role in beta decay and energy production of stars. During the fusion of hydrogen into helium in sun, neutrinos and enormous radiations are produced through weak force. The detailed mechanism of weak force is beyond the scope of this book and for further reading, appropriate books can be referred.
Gravitational, electromagnetic, strong and weak forces are called fundamental forces of nature. It is very interesting to realize that, even for our day-to-day life, we require these four fundamental forces. To put it in simple words: We live on Earth because of Earth’s gravitational attraction on our body. We are standing on the surface of the Earth because of the electromagnetic force between atoms of the surface of the Earth and atoms in our foot. The atoms in our body are stable because of strong nuclear force. Finally, the lives of species on earth depend on the solar energy from the sun and it is due to weak force which plays vital role during nuclear fusion reactions going on in the core of the sun.