Branches Of Physics
Physics as a fundamental science helps to uncover the laws of nature. The language of its expression is mathematics. In ancient times, humans lived with nature – their lifestyles were integrated with nature. They could understand the signals from the movement of the stars and other celestial bodies. They could determine the time to sow and reap by watching the sky. Thus, astronomy and mathematics were the first disciplines to be developed. The chronological development of various branches of physics is presented in Appendix A1.1. The various branches of physics are schematically shown in figure 1.1. The essential focus of different areas is given in Table 1.1.
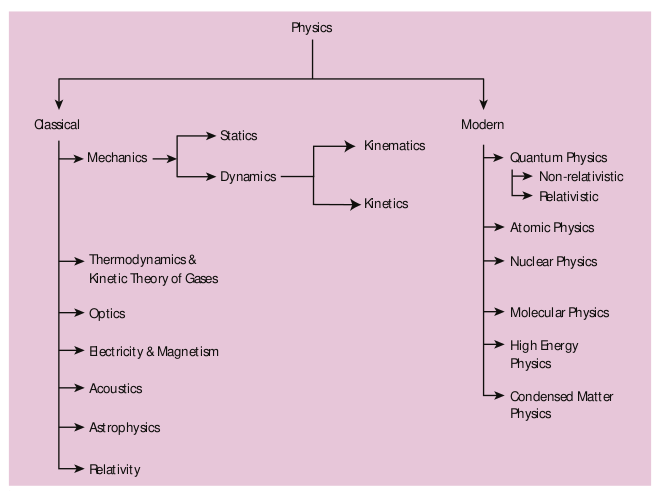
Figure 1.1 Branches of Physics
Some of the fundamental concepts of basic areas of physics are discussed in higher secondary first year physics books volume 1 and 2. Mechanics is covered in unit 1 to 6. Unit 1 gives an idea of the development of physics along with discussion on basic elements such as measurement, units etc. Unit 2 gives the basic mathematics needed to express the impact of physical principles and their governing laws. The impact of forces acting on objects in terms of the fundamental laws of motion of Newton are very systematically covered in unit 3. Work and energy which are the basic parameters of investigation of the mechanical world are presented in unit 4. Unit 5 deals with the mechanics of rigid bodies (in contrast, objects are viewed as point objects in units
Table 1.1 Branches of Physics
| Classical Physics | Refers to traditional physics that was recognized and developed before the beginning of the 20 th century |
|---|---|
| Branch | Major focus |
| 1. Classical mechanics | The study of forces acting on bodies whether at rest or in motion |
| 2. Thermodynamics | The study of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy |
| 3. Optics | The study of light |
| 4. Electricity and magnetism | The study of electricity and magnetism and their mutual relationship |
| 5. Acoustics | The study of the production and propagation of sound waves |
| 6. Astrophysics | The branch of physics which deals with the study of the physics of astronomical bodies |
| 7. Relativity | One of the branches of theoretical physics which deals with |
| the relationship between space, time and energy particularly with respect to objects moving in different ways . | |
| Modern Physics | Refers to the concepts in physics that have surfaced since the beginning of the 20 th century. |
| 1. *Quantum mechanics | The study of the discrete nature of phenomena at the atomic and subatomic levels |
| 2. Atomic physics | The branch of physics which deals with the structure and properties of the atom |
| 3. Nuclear physics | The branch of physics which deals with the structure, properties and reaction of the nuclei of atoms. |
| 4. Condensed matter physics | The study of the properties of condensed materials (solids,liquids and those intermediate between them and densegas). It branches into various sub-divisions including developing fields such as nano science, photonics etc.It covers the basics of materials science, which aims at developing new material with better properties for promising applications. |
| 5. High energy physics | The study of the nature of the particles. |
*Quantum mechanics is a broader approach; classical results can be reproduced in quantum mechanics also. Detailed explanation is beyond the scope of this book.
3 and 4). The basics of gravitation and its consequences are discussed in unit 6. Older branches of physics such as different properties of matter are discussed in unit 7.
The impact of heat and investigations of its consequences are covered in units 8 and 9. Important features of oscillations and wave motion are covered in units 10 and 11.