Androecium
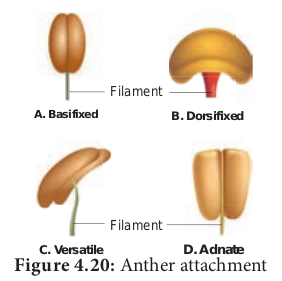
Androecium: Third whorl of flower is the male reproductive part of the flower. It is composed of stamens(microsporophylls). Each Stamen consist of 3 parts, a. Filament b. Anther c. Connective
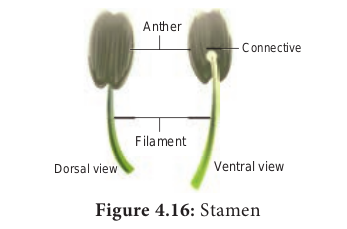
Anther: Upper swollen part with microsporangia.
Filament: Stalk of stamen Connective: Tissue connecting anther lobes with filament Anther typically contains two com partments called thecae (singular theca).Each theca consists of two microsporangia.Two microsporangia fused to form a locule.
Sterile stamens are called Staminodes. Example: Cassia. Distinct: stamens which do not fuse to one another. Free: stamens which do not fuse with other parts of flower. Apostemonous: flowers with stamens that are free and distinct.
Fusion of stamens:
The fusion of stamens fusing among themselves or with other parts of flower. They are of two types.
1.Connation and 2.Adnation
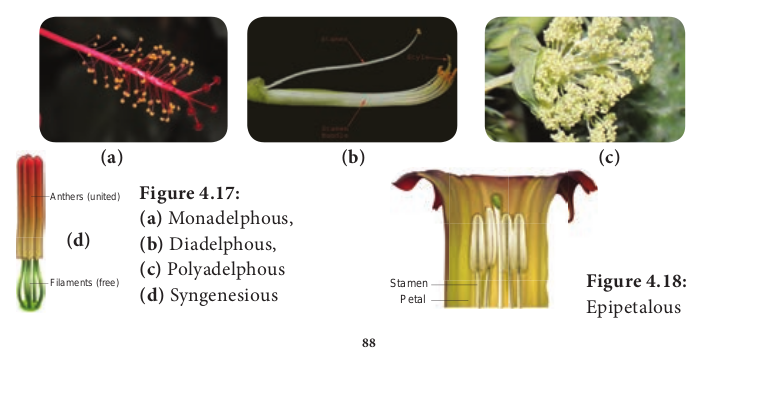
1. Connation: Refers to the fusion of stamens among themselves. It is of 3 types. a. Adelphy. b. Syngenecious. c. Synandrous.
a. Adelphy: Filaments connate into one or more bundles but anthers are free. It may be the following types.
1. Monadelphous: Filaments of stamens connate into a single bundle.Example: Malvaceae (Chinarose, Cotton). 2. Diadelphous: Filaments of stamens connate into two bundles. Example: Fabaceae (pea) and Clitoria.
3. Polyadelphous: Filaments connate into many bundles. Example: Citrus, Bombax
b. Syngenesious: Anthers connate, filaments free. Example: Asteraceae.
c. Synandrous: Filaments and anthers are completely fused. Example: Coccinea.
2. Adnation: Refers to the fusion of stamens with other floral parts. Epipetalous : Stamens are adnate to petals .Example: brinjal, Datura.
a. Episepalous: stamens are adnate to sepals. Example: Grevillea (Silver oak)
b. Epitepalous (epiphyllous): stamens are adnate to tepals. Example: Asparagus.
c. Gynostegium:Connation product of stamens and stigma is called gynostegium. Example: Calotropis and Orchidaceae.
d. Pollinium: Pollen grains are fused together as a single mass Example: Calotropis
Arrangement of stamens relate to length of stamens:
1. Didynamous: Four stamens of which two with long filaments and two with short filaments. Example: Ocimum
2. Tetradynamous: Six stamens of which four with long filaments and two with short filaments. Example: Brassica.
Anther types
1. Monothecal : One lobe with two microsporangia. They are kidney shaped in a cross section. Example: Malvaceae
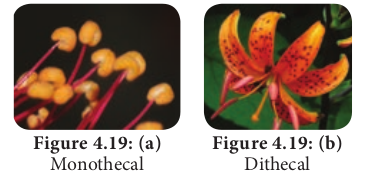
Anther attachment
1. Basifixed:(Innate) Base of anther is attached to the tip of filament. Example: Datura.
2. Dorsifixed: Apex of filament is attached to the dorsal side of the anther. Example: Hibiscus.
3. Versatile: Filament is attached to the anther at midpoint. Example: Grasses.
4. Adnate: Filament is continued from the base to the apex of anther. Example: Nelumbo