Accessory organs
Arrangement of whorls The position of perianth (sepals, petals, tepals) parts relative to one another is called perianth arrangement.
1. Cyclic or whorled: All the floral parts are arranged in definite whorls. Example: Brassica.
2. Acyclic or spiral: The floral parts are arranged in spirals on the elongated fleshy torus. Example: Magnolia.
3. Spirocyclic or hemicyclic: Some parts are in whorls and others parts are in spirals. Example:Annona, Polyalthia
Calyx
Calyx protects the flower in bud stage. Outermost whorl of flower is calyx. Unit of calyx is sepal. Normally green in colour.
1. Fusion:
a. Aposepalous (polysepalous): The flower with distinct sepals. Example: Brassica, Annona.
b. Synsepalous: The flower with united or fused sepals. Example: Hibiscus.
2. Duration of floral parts:
What is the green part of brinjal fruit? Have you seen similar to this in any other fruits?
a. Caducous or fugacious calyx: Calyx that withers or falls off during the early development stage of flower. Example: Papaver.

b. Deciduous:
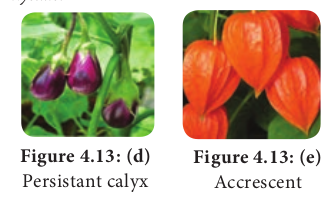
Calyx that falls soon afterthe opening of flower (anthesis) Example: Nelumbo.

d. Accrescent: Calyx that is persistent, grows along with the fruit and encloses the fruit either completely or partially. Example: Physalis.

Corolla
Corolla is the most attractive part in majority of the flowers and is usually brightly coloured. Corolla helps to display the flower and attracts the pollinators.
1. Fusion:
a. Apopetalous (polypetalous): Petals are distinct. Example: Hibiscus.
b. Sympetalous (gamopetalous): Petals are fused. Example: Datura.
Perianth
Can you recall the term homochlamydeous? Undifferentiated calyx and corolla in a flower is called perianth. Each member is called tepal. If the tepals are distinct they are called Apotepalous (Polyphyllous). Example: Allium sativum. Fused tepals are called Syntepalous. (Gamophyllous). Example: Allium cepa.
Lodicule : Reduced scale like perianth in the members of Poaceae is called lodicule.
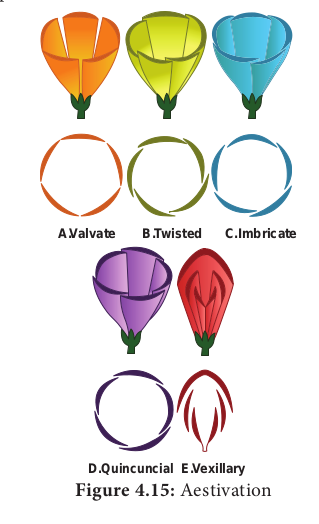
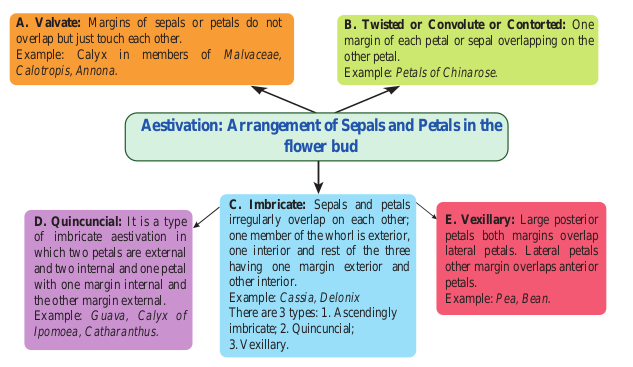
Aestivation:
Arrangement of sepals and petals in the flower bud is said to be aestivation.