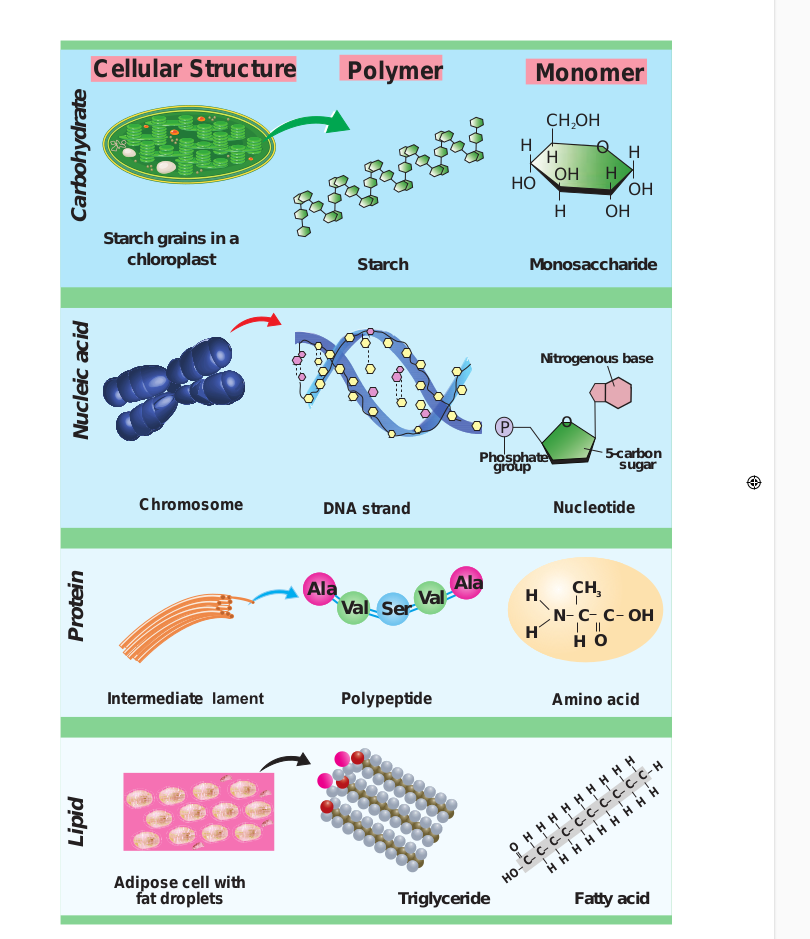
The term lipid is derived from greek word lipos, meaning fat. These substances are not soluble in polar solvent such as water but soluble in non-polar solvents such as benzene, ether, chloroform. This is because they contain long hydrocarbon chains that are non-polar and thus are hydrophobic. The main groups of compounds classified as lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids and waxes.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are composed of single molecule of glycerol bound to 3 fatty acids. These include fats and oils. Fatty acids are long chain hydrocarbons with a carboxyl group at one end which binds to one of the hydroxyl groups of glycerol, thus forming an ester bond. Fatty acids are structural unit of lipids and are carboxylic acid of long chain hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbon can vary in length from 4 – 24 carbons and the fat may be saturated or unsaturated. In saturated fatty acids the hydrocarbon chain is single bonded (Eg. palmitic acid, stearic acid) and in unsaturated fatty acids (Eg. oleic acid, linoleic acid) the hydrocarbon chain is double bonded (one/two/three). In general solid fats are saturated and oils are unsaturated, in which most are globules.